Angular 17 CRUD Operations using Node JS MySQL Tutorial
Hi Developer,
In this tutorial, I will show you crud operations in angular 17 with node js mysql. This example will help you with angular 17 crud with node js and MySQL. I want to show you crud angular 17 node js mysql. This is a simple example of angular 17 crud workflow using node js express mysql.
Angular 17 CRUD with Node.js Express and MySQL Database enables creating, reading, updating, and deleting data in a web application. Angular 17 handles the user interface, Node.js serves as the backend, and MySQL stores the data. CRUD operations involve creating new data, reading existing data, updating data, and deleting data. Together, they form a powerful combination for building dynamic web applications that interact with a database seamlessly. This setup streamlines the process of managing data within web applications, offering users a smooth and efficient experience.
In this example, we are using node.js express to create a posts rest API. We use mysql to store data in mysql database. We then proceed with the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operation for the posts module with the "title" and "body" fields. So, let’s follow the below steps.
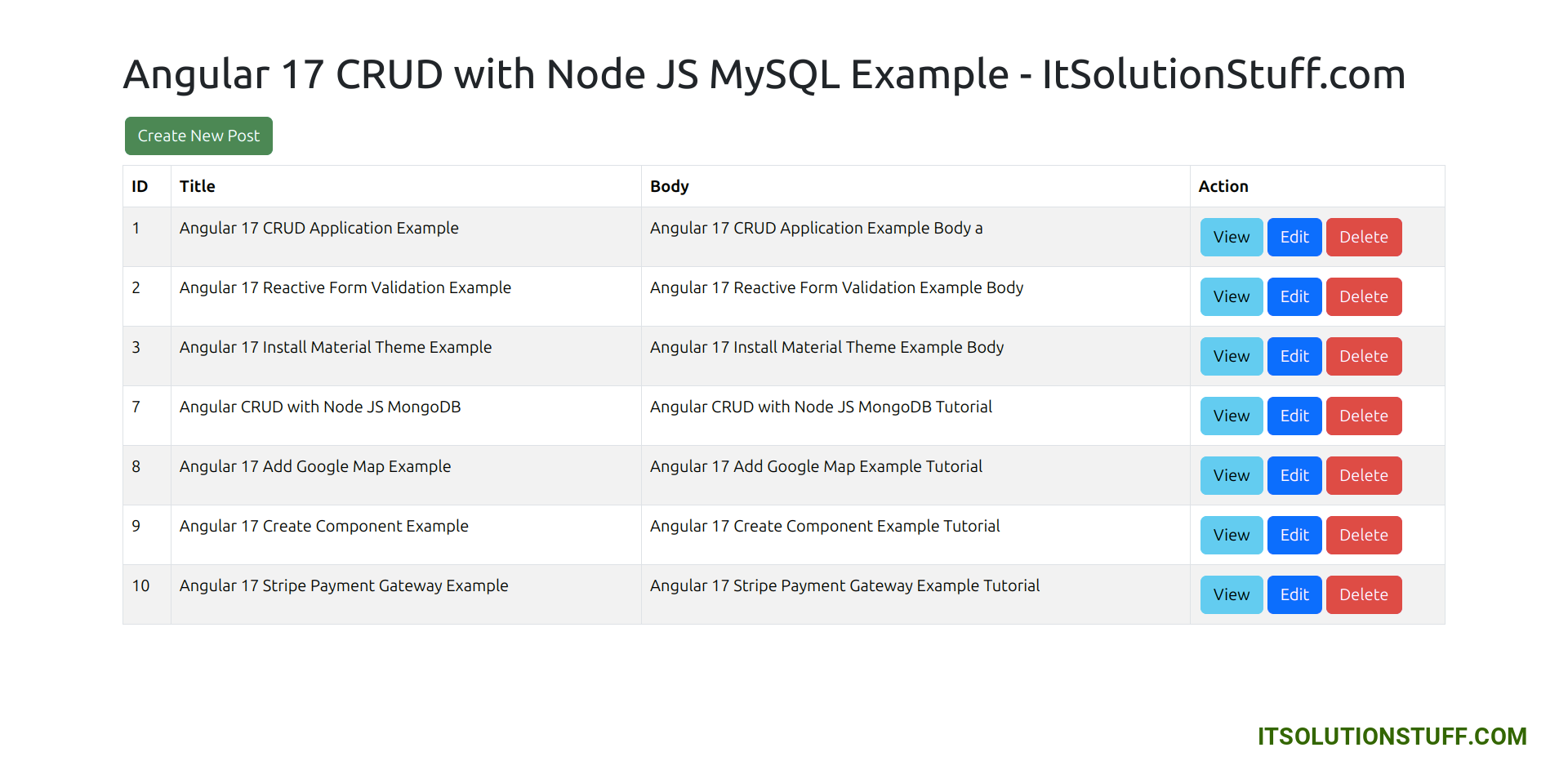
Home Page:
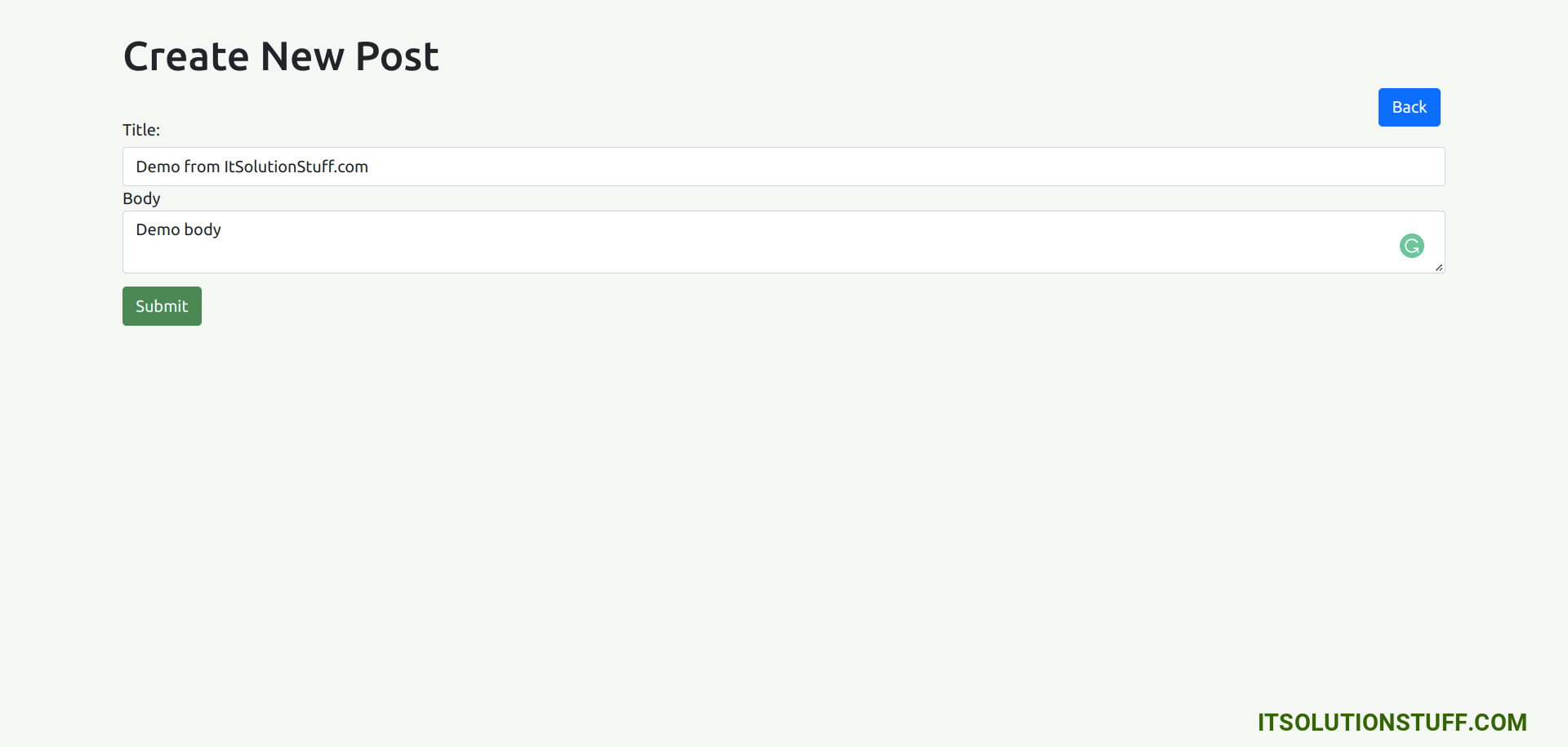
Create Page:
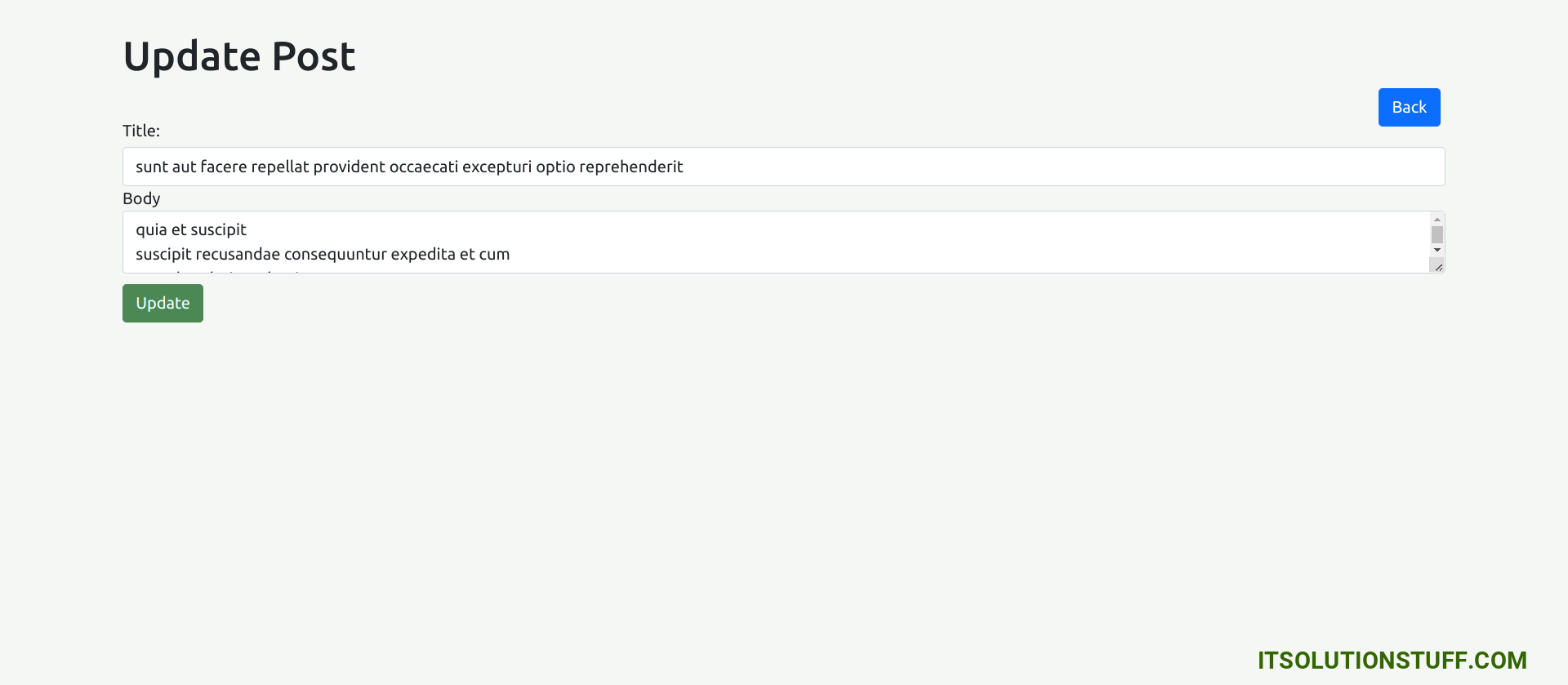
Edit Page:
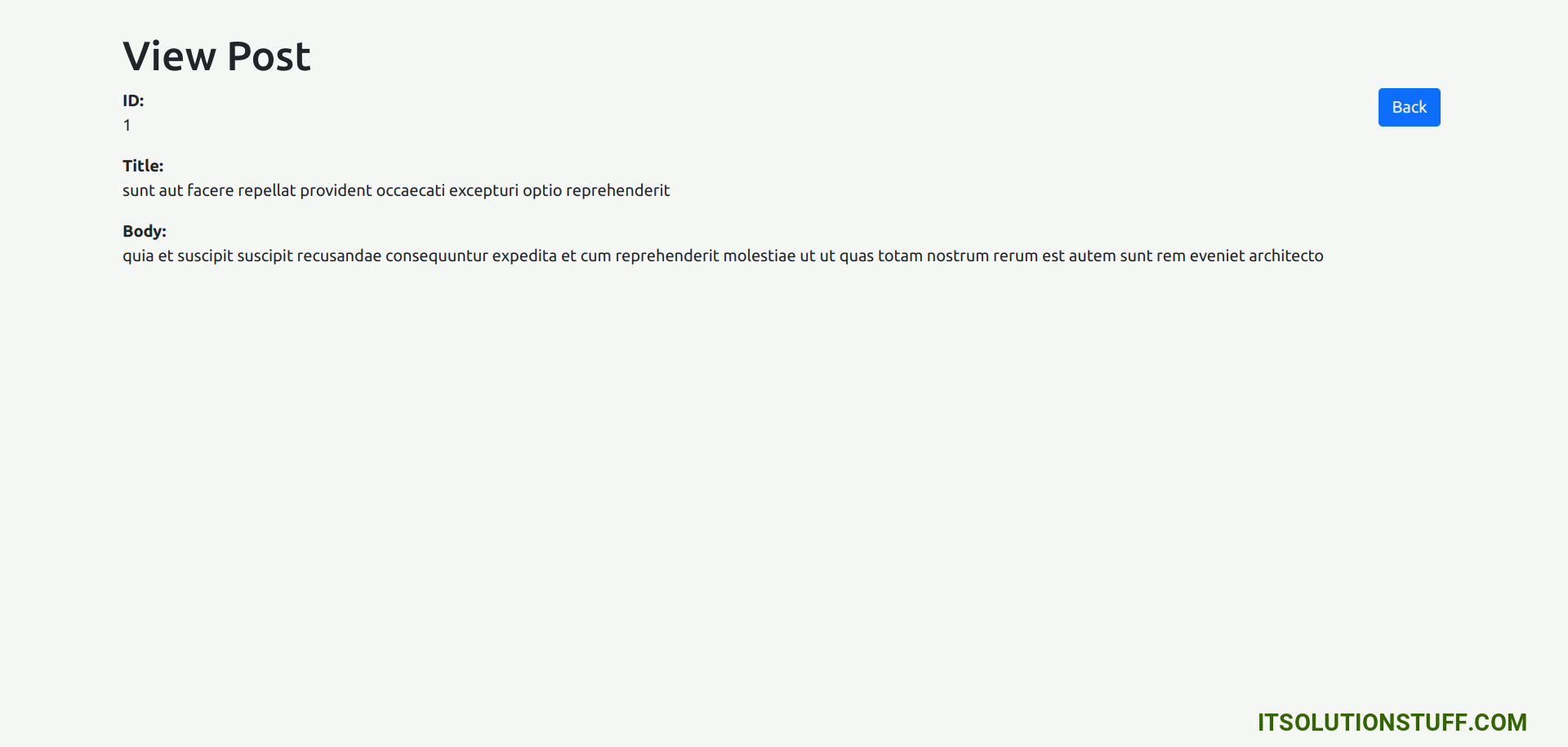
Detail Page:
Step for Angular 17 CRUD with Node JS Express MySQL Database
- Step 1: Create Angular 17 Project
- Step 2: Install Bootstrap
- Step 3: Create Post Module
- Step 4: Create Component For Module
- Step 5: Create Routes
- Step 6: Create Interface
- Step 7: Create Service
- Step 8: Update Component Logic and Template
- Step 9: export provideHttpClient()
- Step 10: Create REST API using Node JS and MySQL
- Run Node JS App
- Run Angular App
Now, let's follow the below step to create crud operations with angular 17.
Step 1: Create Angular 17 Project
You can easily create your angular app using below command:
ng new my-new-app
Step 2: Install Bootstrap
now, we will install bootstrap for our crud application, so let's run bellow command and import it to css file.
npm install bootstrap --save
Now after successfully run above command. let's import it in angular.json file.
angular.json
....
"styles": [
"node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css",
"src/styles.css"
],
.....
Step 3: Create Post Module
After creating successfully app, we need to create post module using angular cli command. angular provide command to create module with routing in angular application. so let's run bellow command to create post module:
ng generate module post
run successfully command, it will create files as like bellow path:
src/app/post/post.module.ts
Step 4: Create Component For Module
Now we will add new component to our post module using bellow command, so let's create index, view, create and edit component for admin module:
ng generate component post/index
ng generate component post/view
ng generate component post/create
ng generate component post/edit
run successfully command, it will create folder with files as like bellow path:
src/app/post/index/*
src/app/post/view/*
src/app/post/create/*
src/app/post/edit/*
Step 5: Create Routes
In this step, we will simply create route for index, create, edit and view using generated new component. so we have to update our app.routes.ts module file as like bellow code:
src/app/app.routes.ts
import { Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { IndexComponent } from './post/index/index.component';
import { ViewComponent } from './post/view/view.component';
import { CreateComponent } from './post/create/create.component';
import { EditComponent } from './post/edit/edit.component';
export const routes: Routes = [
{ path: 'post', redirectTo: 'post/index', pathMatch: 'full'},
{ path: 'post/index', component: IndexComponent },
{ path: 'post/:postId/view', component: ViewComponent },
{ path: 'post/create', component: CreateComponent },
{ path: 'post/:postId/edit', component: EditComponent }
];
Step 6: Create Interface
in this step, we will create interface using angular command for post module. we will use post interface with Observable. so let's create interface with bellow code.
ng generate interface post/post
src/app/post/post.ts
export interface Post {
id: number;
title: string;
body: string;
}
Step 7: Create Service
Here, we will create post service file and we will write and call all web services. we will create getAll(), create(), find(), update() and delete().
we are using http://localhost:8000 web site api for now. in step 10, we are creating a node js app with posts REST API.
Now, let's create post service and put all code for web service method.
ng generate service post/post
src/app/post/post.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpClient, HttpHeaders } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable, throwError } from 'rxjs';
import { catchError } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { Post } from './post';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class PostService {
private apiURL = "http://localhost:3000";
/*------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Http Header Options
--------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------*/
httpOptions = {
headers: new HttpHeaders({
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
})
}
/*------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Created constructor
--------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------*/
constructor(private httpClient: HttpClient) { }
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
getAll(): Observable
{
return this.httpClient.get(this.apiURL + '/posts/')
.pipe(
catchError(this.errorHandler)
)
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
create(post:Post): Observable
{
return this.httpClient.post(this.apiURL + '/posts/create', JSON.stringify(post), this.httpOptions)
.pipe(
catchError(this.errorHandler)
)
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
find(id:number): Observable
{
return this.httpClient.get(this.apiURL + '/posts/' + id)
.pipe(
catchError(this.errorHandler)
)
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
update(id:number, post:Post): Observable
{
return this.httpClient.put(this.apiURL + '/posts/' + id, JSON.stringify(post), this.httpOptions)
.pipe(
catchError(this.errorHandler)
)
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
delete(id:number){
return this.httpClient.delete(this.apiURL + '/posts/' + id, this.httpOptions)
.pipe(
catchError(this.errorHandler)
)
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
errorHandler(error:any) {
let errorMessage = '';
if(error.error instanceof ErrorEvent) {
errorMessage = error.error.message;
} else {
errorMessage = `Error Code: ${error.status}\nMessage: ${error.message}`;
}
return throwError(errorMessage);
}
}
Step 8: Update Component Logic and Template
Now in this step, we will work on our created component for crud application. we create four component for our crud application. now we will go one by one for creating list page, create page, edit page and view page.
so, let's see one by one:
1) List Page Template and Component
now, here we will work on post index component. we will call post service and display it with create, edit, delete and view button. so let's update it.
src/app/post/index/index.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { RouterModule, Router } from '@angular/router';
import { PostService } from '../post.service';
import { Post } from '../post';
@Component({
selector: 'app-index',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, RouterModule],
templateUrl: './index.component.html',
styleUrl: './index.component.css'
})
export class IndexComponent {
posts: Post[] = [];
/*------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Created constructor
--------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------*/
constructor(public postService: PostService, private router: Router) { }
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
ngOnInit(): void {
console.log(this.router.url);
console.log( window.location.href);
this.postService.getAll().subscribe((data: Post[])=>{
this.posts = data;
console.log(this.posts);
})
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
deletePost(id:number){
this.postService.delete(id).subscribe(res => {
this.posts = this.posts.filter(item => item.id !== id);
console.log('Post deleted successfully!');
})
}
}
src/app/post/index/index.component.html
<div class="container">
<h1>Angular 17 CRUD with Node JS MySQL Example - ItSolutionStuff.com</h1>
<a href="#" routerLink="/post/create/" class="btn btn-success">Create New Post</a>
<table class="table table-striped table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Body</th>
<th width="250px">Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor="let post of posts">
<td>{{ post.id }}</td>
<td>{{ post.title }}</td>
<td>{{ post.body }}</td>
<td>
<a href="#" [routerLink]="['/post/', post.id, 'view']" class="btn btn-info">View</a>
<a href="#" [routerLink]="['/post/', post.id, 'edit']" class="btn btn-primary">Edit</a>
<button type="button" (click)="deletePost(post.id)" class="btn btn-danger">Delete</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
You will see preview as like bellow:

2) Create Page Template and Component
now here, we will use reactive form store data into server using web services. so let's update it.
src/app/post/create/create.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { PostService } from '../post.service';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import { ReactiveFormsModule, FormGroup, FormControl, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-create',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, ReactiveFormsModule],
templateUrl: './create.component.html',
styleUrl: './create.component.css'
})
export class CreateComponent {
form!: FormGroup;
/*------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Created constructor
--------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------*/
constructor(
public postService: PostService,
private router: Router
) { }
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
ngOnInit(): void {
this.form = new FormGroup({
title: new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
body: new FormControl('', Validators.required)
});
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
get f(){
return this.form.controls;
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
submit(){
console.log(this.form.value);
this.postService.create(this.form.value).subscribe((res:any) => {
console.log('Post created successfully!');
this.router.navigateByUrl('post/index');
})
}
}
src/app/post/create/create.component.html
<div class="container">
<h1>Create New Post</h1>
<a href="#" routerLink="/post/index" class="btn btn-primary">Back</a>
<form [formGroup]="form" (ngSubmit)="submit()">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">Title:</label>
<input
formControlName="title"
id="title"
type="text"
class="form-control">
<div *ngIf="f['title'].touched && f['title'].invalid" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="f['title'].errors && f['title'].errors['required']">Title is required.</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="body">Body</label>
<textarea
formControlName="body"
id="body"
type="text"
class="form-control">
</textarea>
<div *ngIf="f['body'].touched && f['body'].invalid" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="f['body'].errors && f['body'].errors['required']">Body is required.</div>
</div>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit" [disabled]="!form.valid">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
You will see preview as like bellow:

3) Edit Page Template and Component
now here, we will use reactive form store data into server using web services for update post information. so let's update it.
src/app/post/edit/edit.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { PostService } from '../post.service';
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router';
import { Post } from '../post';
import { ReactiveFormsModule, FormGroup, FormControl, Validators } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-edit',
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule, ReactiveFormsModule],
templateUrl: './edit.component.html',
styleUrl: './edit.component.css'
})
export class EditComponent {
id!: number;
post!: Post;
form!: FormGroup;
/*------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Created constructor
--------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------*/
constructor(
public postService: PostService,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private router: Router
) { }
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
ngOnInit(): void {
this.id = this.route.snapshot.params['postId'];
this.postService.find(this.id).subscribe((data: Post)=>{
this.post = data;
});
this.form = new FormGroup({
title: new FormControl('', [Validators.required]),
body: new FormControl('', Validators.required)
});
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
get f(){
return this.form.controls;
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
submit(){
console.log(this.form.value);
this.postService.update(this.id, this.form.value).subscribe((res:any) => {
console.log('Post updated successfully!');
this.router.navigateByUrl('post/index');
})
}
}
src/app/post/edit/edit.component.html
<div class="container">
<h1>Update Post</h1>
<a href="#" routerLink="/post/index" class="btn btn-primary">Back</a>
<form [formGroup]="form" (ngSubmit)="submit()">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">Title:</label>
<input
formControlName="title"
id="title"
type="text"
[(ngModel)]="post.title"
class="form-control">
<div *ngIf="f['title'].touched && f['title'].invalid" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="f['title'].errors && f['title'].errors['required']">Title is required.</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="body">Body</label>
<textarea
formControlName="body"
id="body"
type="text"
[(ngModel)]="post.body"
class="form-control">
</textarea>
<div *ngIf="f['body'].touched && f['body'].invalid" class="alert alert-danger">
<div *ngIf="f['body'].errors && f['body'].errors['required']">Body is required.</div>
</div>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit" [disabled]="!form.valid">Update</button>
</form>
</div>
You will see preview as like bellow:

4) Detail Page Template and Component
now here, we will display data into server using web services for update post information. so let's update it.
src/app/post/view/view.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { PostService } from '../post.service';
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router';
import { Post } from '../post';
@Component({
selector: 'app-view',
standalone: true,
imports: [],
templateUrl: './view.component.html',
styleUrl: './view.component.css'
})
export class ViewComponent {
id!: number;
post!: Post;
/*------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------
Created constructor
--------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------*/
constructor(
public postService: PostService,
private route: ActivatedRoute,
private router: Router
) { }
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
ngOnInit(): void {
this.id = this.route.snapshot.params['postId'];
this.postService.find(this.id).subscribe((data: Post)=>{
this.post = data;
});
}
}
src/app/post/view/view.component.html
<div class="container">
<h1>View Post</h1>
<a href="#" routerLink="/post/index" class="btn btn-primary">Back</a>
<div>
<strong>ID:</strong>
<p>{{ post.id }}</p>
</div>
<div>
<strong>Title:</strong>
<p>{{ post.title }}</p>
</div>
<div>
<strong>Body:</strong>
<p>{{ post.body }}</p>
</div>
</div>
You will see preview as like bellow:

Now let's update app html view:
src/app/app.component.html
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
Step 9: export provideHttpClient()
In this step, we need to export provideHttpClient() to app.config.ts file. so let's import it as like bellow:
src/app/app.config.ts
import { ApplicationConfig } from '@angular/core';
import { provideRouter } from '@angular/router';
import { routes } from './app.routes';
import { provideAnimations } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { provideHttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [provideRouter(routes), provideAnimations(), provideHttpClient()]
};
Step 10: Create REST API using Node JS and MySQL
In last step, we will create posts rest API using node js, express and mysql.
Setting up MySQL database:
Before proceed to this step, make sure you have installed MySQL in your system.
Create a MySQL database and a table for storing posts:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS node_express_mysql;
USE node_express_mysql;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS posts (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
body TEXT NOT NULL
);
Execute the below command to create new node js app:
mkdir node-express-mysql-rest-api
cd node-express-mysql-rest-api
Then run the below command to setup node js:
npm init -y
Next, execute the following commands to install imperative npm packages which will help us to create REST APIs for our Angular CRUD system:
npm install express mysql body-parser
npm install cors
Next, Create an index.js file and set up the Express server with routes for CRUD operations:
node-express-mysql-rest-api/index.js
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const mysql = require('mysql');
const cors = require('cors');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
/* MySQL Connection */
const db = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: 'root',
database: 'node_express_mysql'
});
/* Connect to MySQL */
db.connect(err => {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log('Connected to MySQL');
});
/* Middleware */
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(cors());
/* Routes */
/* List all posts */
app.get('/posts', (req, res) => {
db.query('SELECT * FROM posts', (err, results) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error fetching posts');
return;
}
res.json(results);
});
});
/* Create a new post */
app.post('/posts/create', (req, res) => {
const { title, body } = req.body;
db.query('INSERT INTO posts (title, body) VALUES (?, ?)', [title, body], (err, result) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error creating post');
return;
}
const postId = result.insertId;
db.query('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = ?', postId, (err, result) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error fetching created post');
return;
}
res.status(201).json(result[0]);
});
});
});
/* Get a specific post */
app.get('/posts/:id', (req, res) => {
const postId = req.params.id;
db.query('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = ?', postId, (err, result) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error fetching post');
return;
}
if (result.length === 0) {
res.status(404).send('Post not found');
return;
}
res.json(result[0]);
});
});
/* Update a post */
app.put('/posts/:id', (req, res) => {
const postId = req.params.id;
const { title, body } = req.body;
db.query('UPDATE posts SET title = ?, body = ? WHERE id = ?', [title, body, postId], err => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error updating post');
return;
}
db.query('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = ?', postId, (err, result) => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error fetching updated post');
return;
}
res.json(result[0]);
});
});
});
/* Delete a post */
app.delete('/posts/:id', (req, res) => {
const postId = req.params.id;
db.query('DELETE FROM posts WHERE id = ?', postId, err => {
if (err) {
res.status(500).send('Error deleting post');
return;
}
res.status(200).json({ msg: 'Post deleted successfully' });
});
});
/* Start server */
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${port}`);
});
Run Node JS App:
All the required steps have been done, now you have to type the given below command and hit enter to run the Node.js app:
node index.js
Now, it's enable http://localhost:3000 URL to access created REST API.
Run Angular App:
All the required steps have been done, now you have to type the given below command and hit enter to run the Angular app:
ng serve
Now, Go to your web browser, type the given URL and view the app output:
http://localhost:4200/post
I hope it can help you...

